
June 18, 2024
Tokenization in payments: Network vs PCI tokenization compared
- What is network tokenization?
- What is PCI tokenization?
- What is the difference between PCI tokenization and network tokenization?
- What is the difference between network tokenization and gateway tokenization?
- What is the difference between network tokenization and acquirer tokenization?
- What is the difference between network token and merchant token?
- Tokenization in payments FAQs
Securing payment information is a critical concern for businesses and consumers in today’s digital economy. Tokenization stands out as a robust solution among the various strategies employed to protect sensitive data. However, tokenization is not monolithic; it encompasses different methods tailored to specific needs and regulatory requirements. Two key forms of tokenization are network tokenization and PCI tokenization. This article explores the nuances of these two methods, shedding light on their unique characteristics, benefits, and practical applications, helping businesses choose the best approach for their security needs.
What is network tokenization?
Definition and explanation
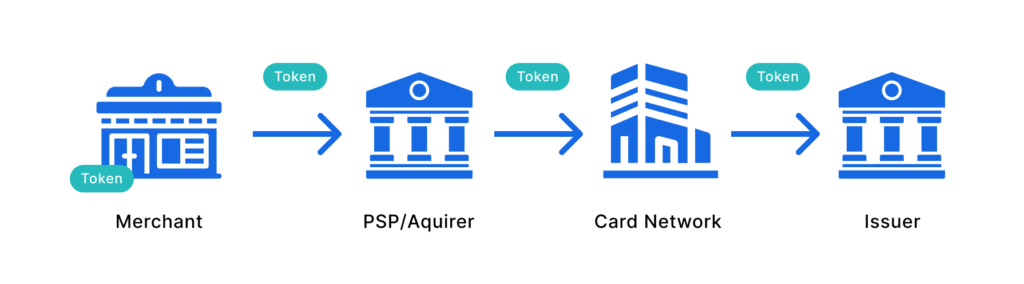
Network tokenization involves replacing sensitive card information with a unique token generated and managed by the payment network (e.g., Visa, MasterCard). This token can be used across multiple merchants and transactions, providing a consistent and secure way to handle payments.
In network tokenization, the payment network stores the actual card details securely. The network generates a token representing the card details when a transaction is initiated. This token is then used for the transaction, ensuring that the card information is not exposed during the process. This method enhances security by reducing the risk of data breaches and fraud.
Benefits
Network tokenization offers several advantages:
- Enhanced security: Using tokens instead of actual card information significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and fraud.
- Interoperability: Tokens can be used across multiple merchants and transactions, providing a seamless payment experience.
- Compliance: Network tokenization helps businesses comply with various regulatory requirements, as sensitive data is not stored or transmitted during transactions.

For a deeper understanding of network tokenization, you can refer to our comprehensive eGuide on network tokenization.
What is PCI tokenization?
Definition and explanation
PCI tokenization involves replacing sensitive card information with a token generated and managed by a PCI-compliant service provider. This method focuses on helping businesses reduce their PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) scope by ensuring that card data is not stored or processed in their systems.
In PCI tokenization, the card details are stored in a secure token vault managed by the service provider. The provider generates a token representing the card details when a transaction is initiated. This token is then used for the transaction, ensuring that the card information is not exposed during the process. PCI tokenization helps businesses achieve compliance with PCI DSS requirements, reducing the burden of managing sensitive data.
Benefits
PCI tokenization provides several key benefits:
- PCI DSS compliance: This service helps businesses meet PCI DSS requirements by ensuring that card data is not stored or processed in their systems.
- Security: Reduces the risk of data breaches and fraud by using tokens instead of actual card information.
- Simplified operations: By outsourcing the management of sensitive data to a PCI-compliant service provider, businesses can focus on their core operations.
What is the difference between PCI tokenization and network tokenization?
Key differences
While both PCI tokenization and network tokenization aim to enhance payment security by replacing sensitive card information with tokens, they differ in their scope and implementation:
- Scope: PCI tokenization focuses on reducing businesses’ PCI DSS scope by ensuring that card data is not stored or processed in their systems. Network tokenization, on the other hand, provides a broader scope by allowing tokens to be used across multiple merchants and transactions.
- Management: In PCI tokenization, tokens are managed by a PCI-compliant service provider, while in network tokenization, tokens are managed by the payment network.
- Interoperability: Network tokens can be used across merchants and transactions, providing a seamless payment experience. PCI tokens are typically limited to specific use cases within a single merchant’s environment.
Use cases
- PCI tokenization: Ideal for businesses that need to comply with PCI DSS requirements and want to reduce the burden of managing sensitive data.
- Network tokenization: Suitable for businesses that operate across multiple merchants and require a consistent and secure payment experience.
What is the difference between network tokenization and gateway tokenization?
Definitions
- Network tokenization: Involves replacing sensitive card information with a token generated and managed by the payment network, used across multiple merchants and transactions.
- Gateway tokenization: Involves replacing card information with a token generated by the payment gateway, typically used within the context of a single merchant or transaction.
Key differences
- Scope: Network tokenization provides a broader scope, allowing tokens to be used across multiple merchants and transactions. Gateway tokenization is more limited in scope, typically confined to a single merchant or transaction.
- Management: The payment network manages network tokens, while the payment gateway manages gateway tokens.
For more detailed insights, download our comprehensive eGuide on network tokenization.
What is the difference between network tokenization and acquirer tokenization?
Definitions
- Acquirer tokenization: Involves replacing card information with a token generated by the acquiring bank and used within the acquiring bank’s ecosystem.
- Network tokenization: Involves replacing card information with a token generated by the payment network, used across multiple merchants and transactions.
Key differences
- Scope: Acquirer tokenization is limited to the acquiring bank’s ecosystem, while network tokenization has a broader scope, allowing tokens to be used across multiple merchants and transactions.
- Management: The acquiring bank manages acquirer tokens, while the payment network manages network tokens.
What is the difference between network token and merchant token?
Definitions
- Merchant token: A token generated by the merchant or their payment processor, used within the merchant’s ecosystem.
- Network token: A token generated by the payment network, used across multiple merchants and transactions.
Key differences
- Scope: Merchant tokens are limited to the merchant’s ecosystem, while network tokens can be used across multiple merchants and transactions.
- Management: Merchant tokens are managed by the merchant or their payment processor, while network tokens are managed by the payment network.
Tokenization in payments FAQs
How does tokenization enhance payment security?
Tokenization enhances payment security by replacing sensitive card information with tokens without exploitable value, reducing the risk of data breaches and fraud.
Can network tokens be used across different merchants?
Yes, network tokens can be used across different merchants and transactions, providing a seamless and secure payment experience.
What are the compliance benefits of PCI tokenization?
PCI tokenization helps businesses meet PCI DSS requirements by ensuring that card data is not stored or processed in their systems, reducing the scope of compliance.
Is gateway tokenization more secure than network tokenization?
Both methods offer security benefits, but network tokenization provides a broader scope and interoperability, making it suitable for use across multiple merchants and transactions.
How do businesses choose between different types of tokenization?
When choosing between different types of tokenization, businesses should consider their specific needs, such as compliance requirements, scope of operations, and desired level of interoperability.
Understanding the differences between network tokenization and PCI tokenization is crucial for businesses looking to enhance their payment security and compliance. Each method offers unique benefits and serves different purposes within the payment ecosystem. By carefully evaluating their needs and the features of each tokenization method, businesses can make informed decisions to protect sensitive payment information.
If you want to learn more about how tokenization can benefit your business, contact Gr4vy to book a demo and discover how our payment orchestration solutions can help you enhance security and efficiency in your payment processes.